The body's reaction to infection may result in sepsis, a potentially fatal medical illness. When the human body detects an infection, it usually responds by pumping chemicals into the circulation to kill the invaders. But with sepsis, the body responds excessively, leading to systemic inflammation and possible organ failure. Although it is most often caused by the body's reaction to bacterial infections, viral and fungal infections may also lead to this illness. The ability to recognize and treat sepsis early may greatly improve results and reduce the risk of complications and mortality, making knowledge of the condition essential.
Understanding Sepsis
The Underlying Causes of Sepsis
Sepsis is a potentially fatal illness caused by the body's extreme reaction to infection. Infections of many kinds, such as bacteria, viruses, and fungi, may set it off. Sepsis usually develops from a more localized illness, including pneumonia, a UTI, or a skin infection. To further understand how these infections lead to sepsis, consider the following:
Bacterial Infections
Pneumonia and UTIs are two common instances of bacterial illnesses that may lead to sepsis. Pneumonia and UTIs are both bacterial illnesses that may progress to a point where they invade the bloodstream. The vital need of early detection and treatment for these localized infections is highlighted by the fact that once germs enter the circulation, the body's inflammatory response may spiral out of control, possibly terminating in sepsis.
Viral Infections
Sepsis may also be caused by viruses, however this is far less often. Certain viruses may cause systemic inflammation and tissue damage. These viral infections may develop into sepsis if not treated properly. All the more reason to keep an eye out for signs of sepsis and act quickly if you suspect it could be developing, especially in situations of viral diseases.
Fungal Infections
Fungal infections are a less frequent cause of sepsis than those caused by bacteria or viruses, but they can occur. These fungal infections may start off small, but if they aren't treated and are allowed to develop, they may cause the hyperactive inflammatory response seen in sepsis. To avoid the potentially fatal effects of sepsis, it is crucial to detect and treat fungal infections and other diseases as soon as possible.
The Importance of Knowing about Sepsis
Because of its rapid progression and the terrible consequences it may have if not treated quickly, sepsis education and awareness are of paramount importance. The likelihood of recovery and the likelihood of long-term consequences may be greatly improved with early detection and medical intervention. The public's understanding of sepsis is crucial to the development of early and successful treatment techniques, which in turn reduce the condition's devastating effects.
Identifying the Symptoms of Sepsis
Early Signs and Symptoms
Due to their subtlety, the early signs of sepsis are frequently misdiagnosed as other, less serious illnesses. Apparently infectious symptoms include irregular heartbeat or blood pressure, mental confusion, difficulty breathing, high temperature, and shaking. These signs and symptoms reflect the body's overreaction to an infection and should not be ignored since prompt diagnosis and treatment may greatly improve the outcome.
Progression and Severe Symptoms
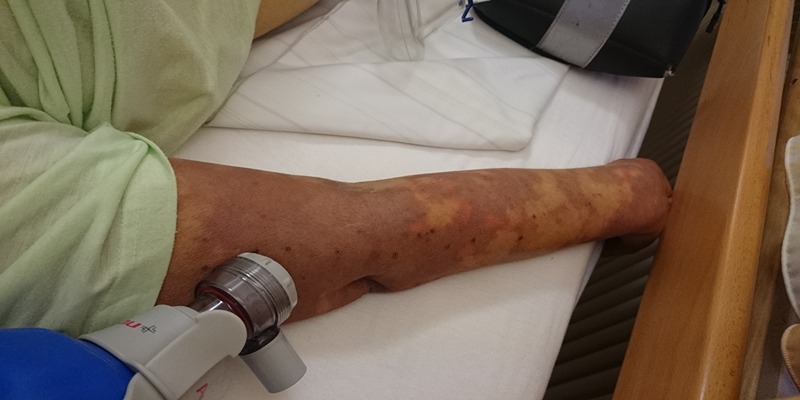
Progressive sepsis may cause a decline in urine, severe muscular discomfort, skin discoloration, and eventually, coma. Septic shock, marked by severe reductions in blood pressure and changes in cellular metabolism, may develop suddenly in such cases. These severe symptoms are a result of the body's heightened reaction to infection, which has caused extensive organ malfunction. The worsening of symptoms calls for urgent medical care to avoid further decline and perhaps permanent harm. The catastrophic effects of advanced sepsis may be lessened with the help of knowledge about the disease's course and recognition of severe symptoms.
Sepsis Treatment
Immediate Medical Attention
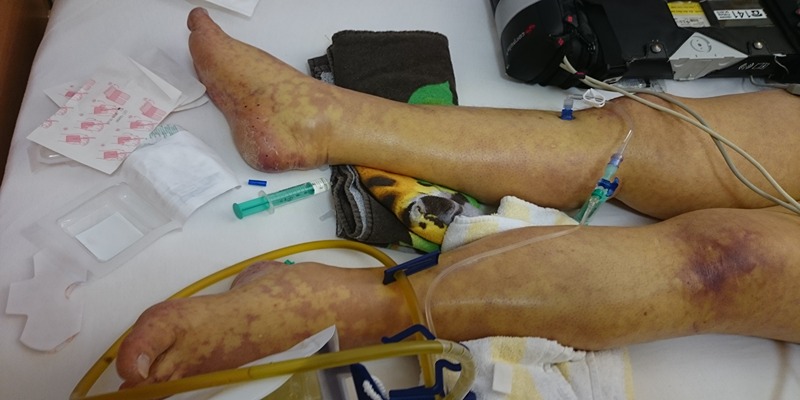
In cases of sepsis, prompt and precise medical intervention is essential. In order to determine the source of an illness and begin appropriate treatment, prompt medical intervention is essential. Rapid administration of intravenous (IV) fluids and antibiotics is standard practice for stabilizing the patient and treating the illness. Severe damage and organ failure may occur if sepsis is not treated immediately, thus a quick medical response is essential.
Treatment Options and Management
After the patient has been stabilized, sepsis management entails a variety of individualized treatment approaches. Medications that increase blood pressure, maintain blood sugar, or lower inflammation may fall into this category. In addition to treating the underlying cause of the organ malfunction and preventing subsequent consequences, sepsis therapy includes constant monitoring and supportive care. The significance of all-encompassing medical care cannot be overstated when discussing the multimodal strategy used to treat sepsis and so reduce its devastating effects and promote recovery.
The Critical Role of Early Detection
Importance of Timely Intervention
It is impossible to overestimate the value of rapid response in sepsis situations. Controlling the infection and avoiding sepsis from progressing to a more severe condition, such septic shock, depend on prompt diagnosis and medical intervention. With prompt medical attention, life-threatening consequences like organ failure may be avoided by administering therapies like antibiotics and fluids.
Impact on Recovery and Outcomes
Patient outcomes and the likelihood of a full recovery are significantly related to how quickly sepsis is diagnosed and treated. Treatment that is both prompt and intense may greatly improve survival chances and lessen the probability of permanent injury or disability. Maximizing the efficacy of therapies and improving the prognosis for those afflicted by sepsis, therefore, requires a proactive approach to identification and treatment.
Preventive Measures Against Sepsis
Risk Reduction Strategies
Prevention of sepsis relies heavily on the use of risk mitigation methods. The development of sepsis may be prevented by taking precautions such as practicing excellent hygiene, getting the appropriate vaccinations, and getting medical assistance quickly if an infection develops. It is also important to take precautions while treating wounds, particularly in those with chronic medical disorders or impaired immune systems, in order to reduce the likelihood of getting sepsis.
Importance of Public Awareness and Education
Preventing sepsis requires raising public awareness and educating people about the condition. Individuals may delay the progression of sepsis by seeking medical attention as soon as possible if they are aware of the symptoms and the significance of doing so. The community's capacity to detect and react rapidly to sepsis, a potentially fatal infection, is greatly improved through public awareness campaigns and educational activities.
Conclusion
Localized diseases like pneumonia or UTIs may progress into systemic sepsis, which is commonly driven by bacterial, viral, or fungal infections. Some of the first symptoms include disorientation, high temperature, and heart palpitations. Reduced urine output, muscular soreness, and skin discoloration are some of the severe symptoms. Getting timely medical care is essential. Rapid intervention, including intravenous fluids and antibiotics, is necessary for treatment, as are patient-specific plans. In order to improve results, decrease the likelihood of irreversible damage, and delay the onset of complications such septic shock, early identification is crucial. In order to improve survival rates and decrease complications, early recognition and treatment of sepsis requires public awareness and education.